
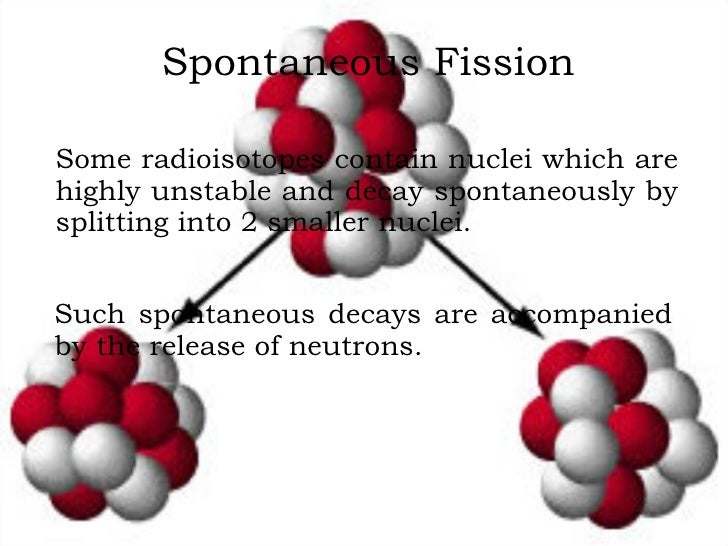
Because the nuclear binding energy of the elements reaches its maximum at an atomic mass number greater than about 58 atomic mass units (u), spontaneous breakdown into smaller nuclei and a few isolated nuclear particles becomes possible at heavier masses.īecause of the constraints in forming the daughter fission-product nuclei, spontaneous fission into known nuclides becomes theoretically possible (that is, energetically possible) for some atomic nuclei with atomic masses greater than 92 atomic mass units (a.m.u.), with the probability of spontaneous fission increasing as the atomic mass number increases above this value. Your insights and inferences are all on track, but I don’t think anyone will soon attempt to provide empirical validation of the presence of spontaneous fission–induced radioactive atoms.Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of radioactive decay that is found only in very heavy chemical elements. Lastly, recognizing that there are few radioactive atoms being produced by the neutron capture that you postulate, we would be facing a monumental task requiring extreme sensitivity to be able to identify such atoms in a sea of neighboring atoms, most of which are stable but many of which are naturally radioactive. Also, some neutrons may be captured by nuclei that lead to stable products, and some radioactive products may have short half-lives, causing them to disappear fairy quickly. Third, the probability of a neutron being absorbed by a given available nucleus is often quite small, the magnitude being governed by the size of the nucleus' cross section, and many species exhibit rather small cross sections. The farther neutrons have to travel from their locus of production before being captured, the lower will be their intensity (measured by their fluence rate), and the lower will be any induced radioactivity produced. It becomes likely then that a large fraction of the few neutrons produced will end up leaving the material in which they were produced and being captured by some nucleus in some other material.

Second, about two to three neutrons are produced per fission, and these neutrons must lose significant energy, usually by scattering reactions, before they are likely to be captured by a nucleus that might become radioactive upon such capture. Beyond that, the spontaneous fission decay mode represents a very small probability event with about five out of every 10 million decays being a spontaneous fission event and the remainder of the decays being by alpha particle emission. Among some of the most pertinent are first, the half-life of uranium-238 ( 238U), the most dominant uranium isotope in the materials of concern, is very long, about 4.5 billion years, resulting in a low decay rate for any uranium in the materials. As you have also surmised, the major reason this induced radioactivity is not evident either in the material containing the uranium or in the immediate surroundings is that there is extremely little of such activity being produced.Ī number of factors contribute to this reality. Additionally, some of these neutrons do have a finite probability of being captured by some stable nuclei and possibly producing some radioactive atoms. Your observation that spontaneous fission of uranium is a potential source of neutrons is true.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
